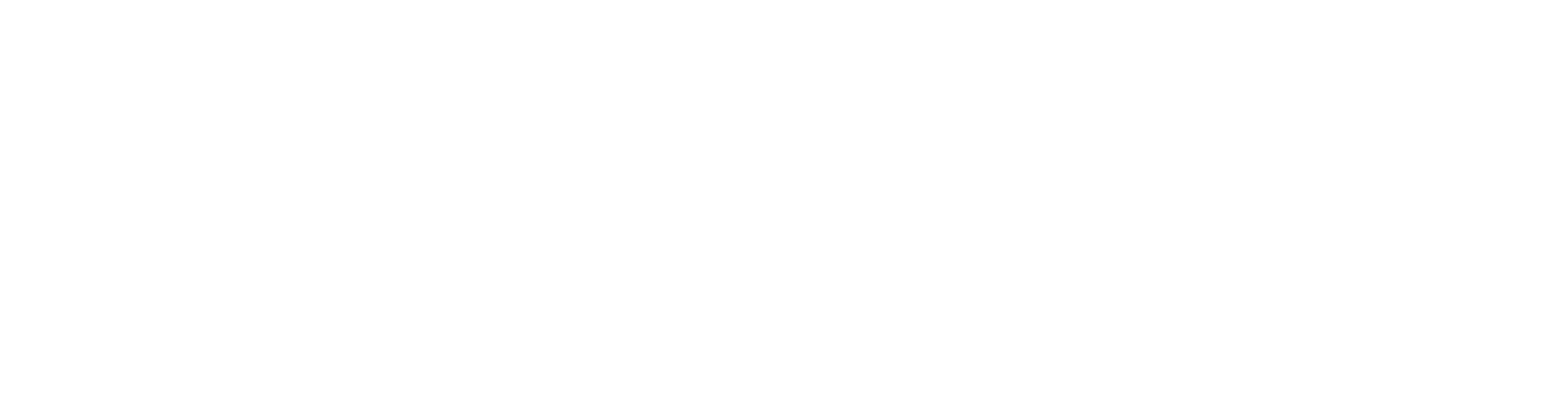Have you ever been mesmerized by the beauty of a company logo? Or been impressed by the ease of use of an app on your phone? Behind it all, there is an art called design that plays an important role in creating attractive and useful products and services.
So what is design?

Design is not just about aesthetics, but also about function, communication and persuasion. Good design can improve people's quality of life, solve problems, and strengthen a brand's identity.
This article will take you through the world of design, from the definition of design, its function, purpose, principles, to the methods used by designers in creating extraordinary works.
Design Definition
Definition Design design has a fairly broad and diverse definition, depending on the context and point of view. Here are some commonly used definitions of design:
1. Big Indonesian Dictionary (KBBI)
- Design: design; sketch; construction drawing; shape
- Design: An activity that aims to determine and shape the form, function, and meaning of an object or system.
- Design: A vehicle to help implement innovation in various industrial and business activities.
- Design: A process that aims to create products and services that are useful, usable, and enjoyable for users.
- Design: A process that aims to give meaning and purpose to an object or system.
From some of the definitions above, it can be concluded that the definition of design is a creative process that results in the design or form of an object or system that has the following function, aesthetics, and meaning that is beneficial to the user.
Design can be defined as the process of planning, creating and arranging elements to create something functional, aesthetic and communicative. Design is all around us, from simple objects like the cups we use to drink from, to grand buildings like skyscrapers.
Good design is not only beautiful to look at, but also easy to use and able to convey messages effectively. Functional design helps us to do our daily activities more easily and efficiently.
Aesthetic design can improve the quality of life and provide a sense of pleasure and comfort for its users. Communicative design can convey information and messages clearly and attractively, helping us make decisions and understand things better.
In short, design is an essential element of everyday life that plays a huge role in improve the quality of life and make the world around us more beautiful, functional and communicative.

Design Function
To get a sense of design, we must also talk about its function. Design is not just about creating beautiful objects, but also about providing function, meaning, and positive influence to people's lives. Here are some of the main functions of design:
1. Aesthetic Function:
A beautiful and visually appealing design can bring a sense of pleasure and comfort to its users. It can improve the quality of life and make the world around us more beautiful. Some examples of the aesthetic function of a design include:
- A beautiful home interior design can provide a sense of calm and comfort for its residents.
- Necklaces with unique and elegant designs can be attractive accessories to enhance your appearance.
- The right combination of colors and clothing pieces can make someone look more stylish and confident.
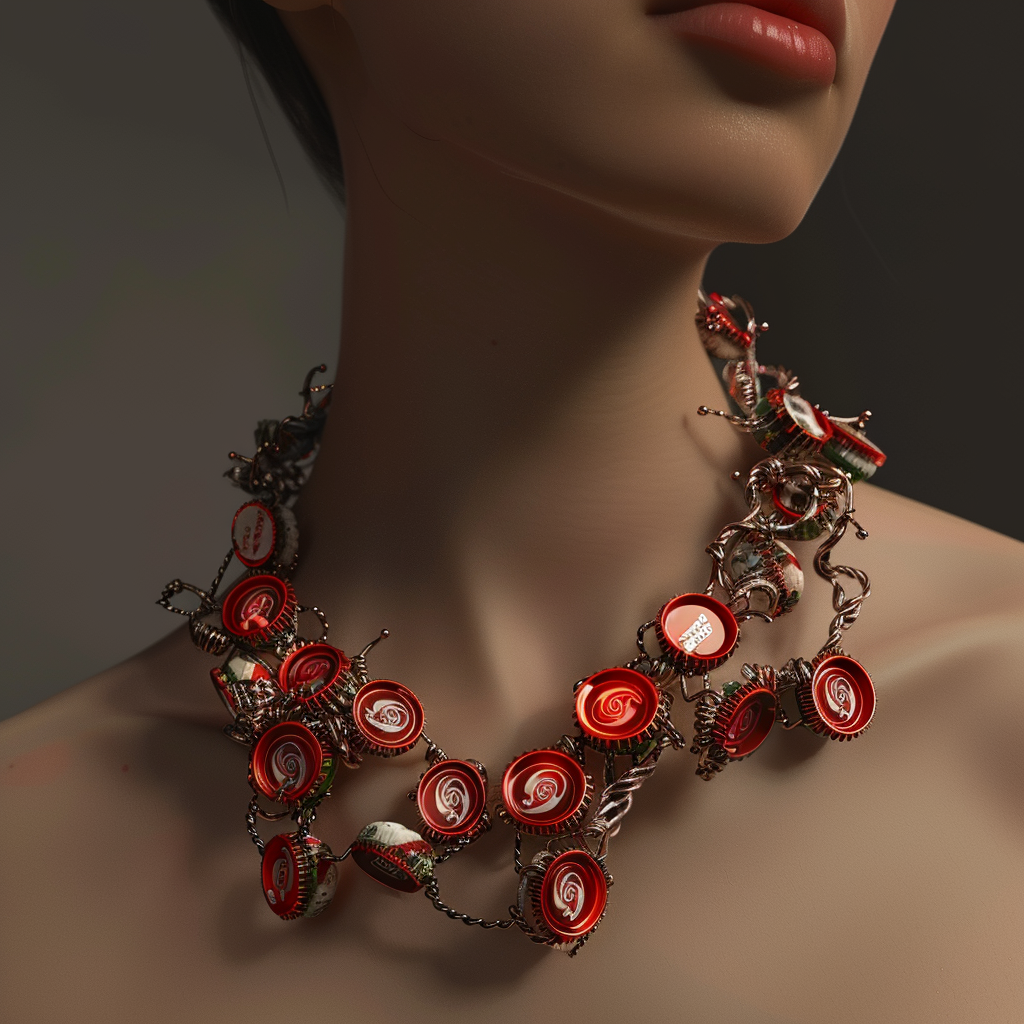

Aesthetic design function can turn bottle caps and copper wire into a beautiful necklace
2. Functionality:
Functional design helps us perform our daily activities more easily and efficiently. For example, an ergonomic chair design can help prevent back pain when sitting for long periods of time.
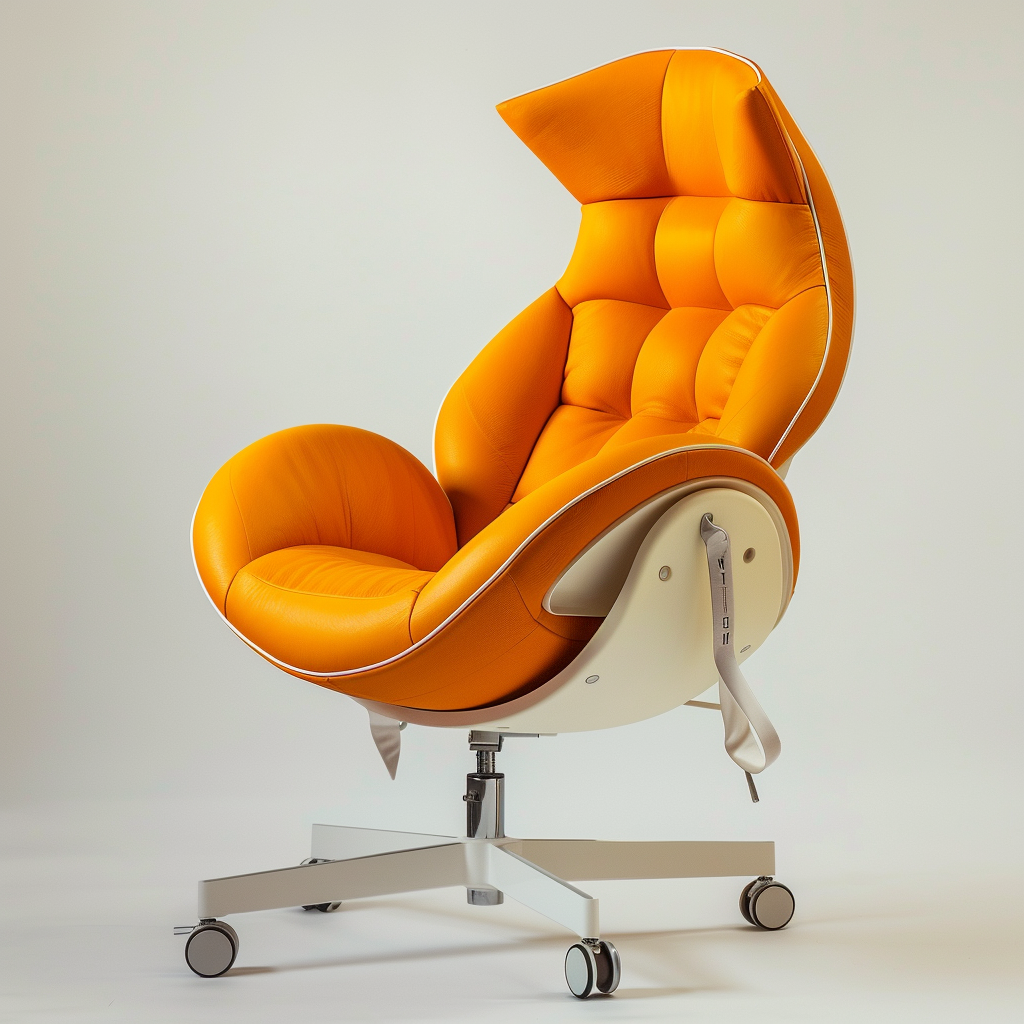

Functionality in a mango-inspired ergonomic work chair
3. Communicative Function:
Design can be used to convey messages and information to users in a clear and attractive way. For example, an informative product packaging design can help consumers choose the right product.
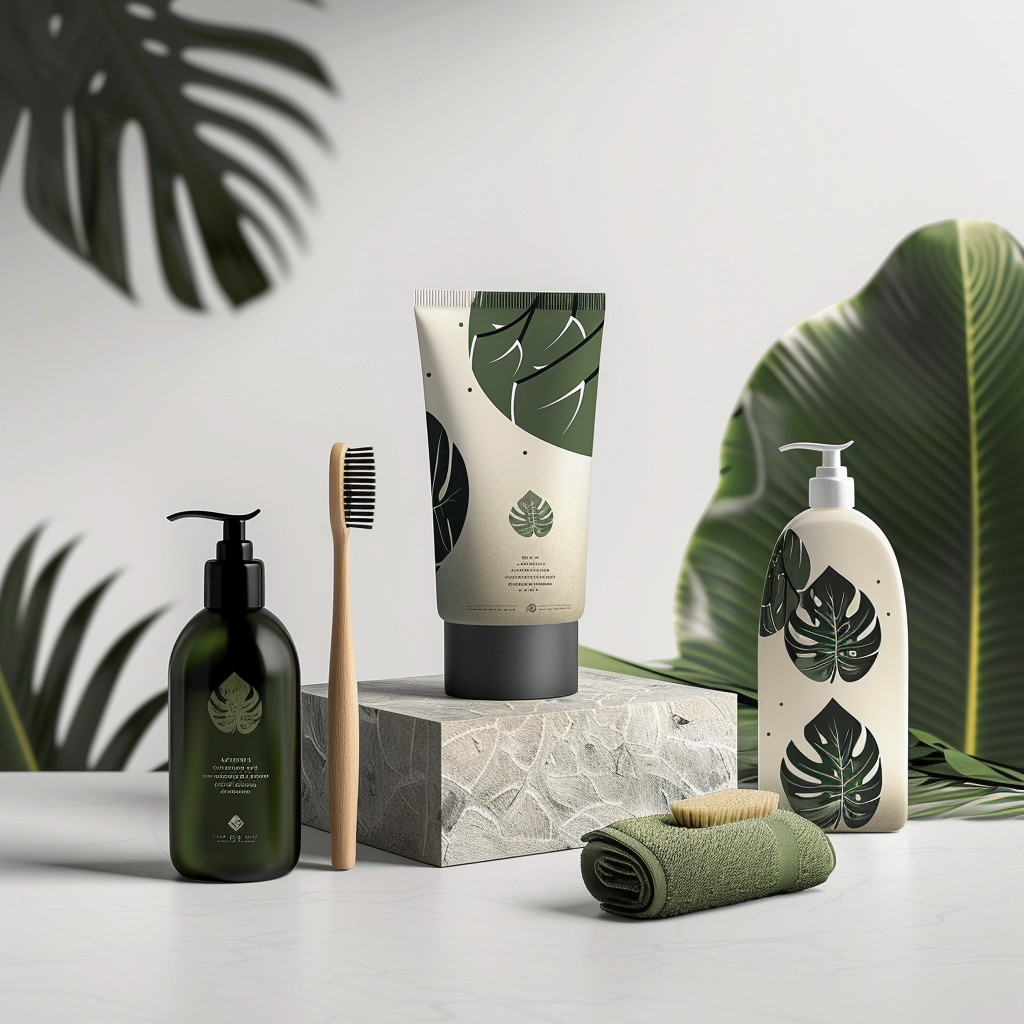

The communicative function in the design allows users to feel that these toiletries are made using natural materials.
4. Persuasive Function:
Design can be used to influence and encourage users to take certain actions. For example, an attractive ad design can encourage consumers to buy the advertised product.

In 2018, KFC London experienced an ingredient crisis due to changes in their supply chain system. KFC made an advertisement to apologize to its loyal customers.
These four design functions are interrelated and cannot be separated from one another. A good design must have a balance between these four functions in order to provide maximum benefits to its users.
Did you know that good design can sometimes go unnoticed? Like the map of the public transportation system, the London Underground, which was altered by Harry Beck in 1931.

Design Intent
To know about the definition of design we must also know its purpose. Design not only aims to create beautiful objects, but also to achieve greater goals in human life. Here are some of the main purposes of design:
1. Improving the Quality of Human Life:
Good design can help improve the quality of human life in many ways, such as:
- Make products and services easier to use and more efficient. For example, ergonomic chair design can help prevent back pain when sitting for long periods of time.
- Creating a more comfortable and pleasant space to live and work in. For example, a modern and minimalist office interior design can increase employee productivity.
- Making products and services safer and more environmentally friendly. For example, fuel-efficient car designs can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Solving Problems and Meeting Human Needs:
Design can be used to solve problems and meet human needs in various fields, such as:
- Health design: Innovative medical aid designs can help improve patients' quality of life.
- Educational design: An interactive and engaging learning space design can help increase students' interest in learning.
- Transportation design: The design of efficient and user-friendly public transportation systems can help reduce congestion and pollution in big cities.
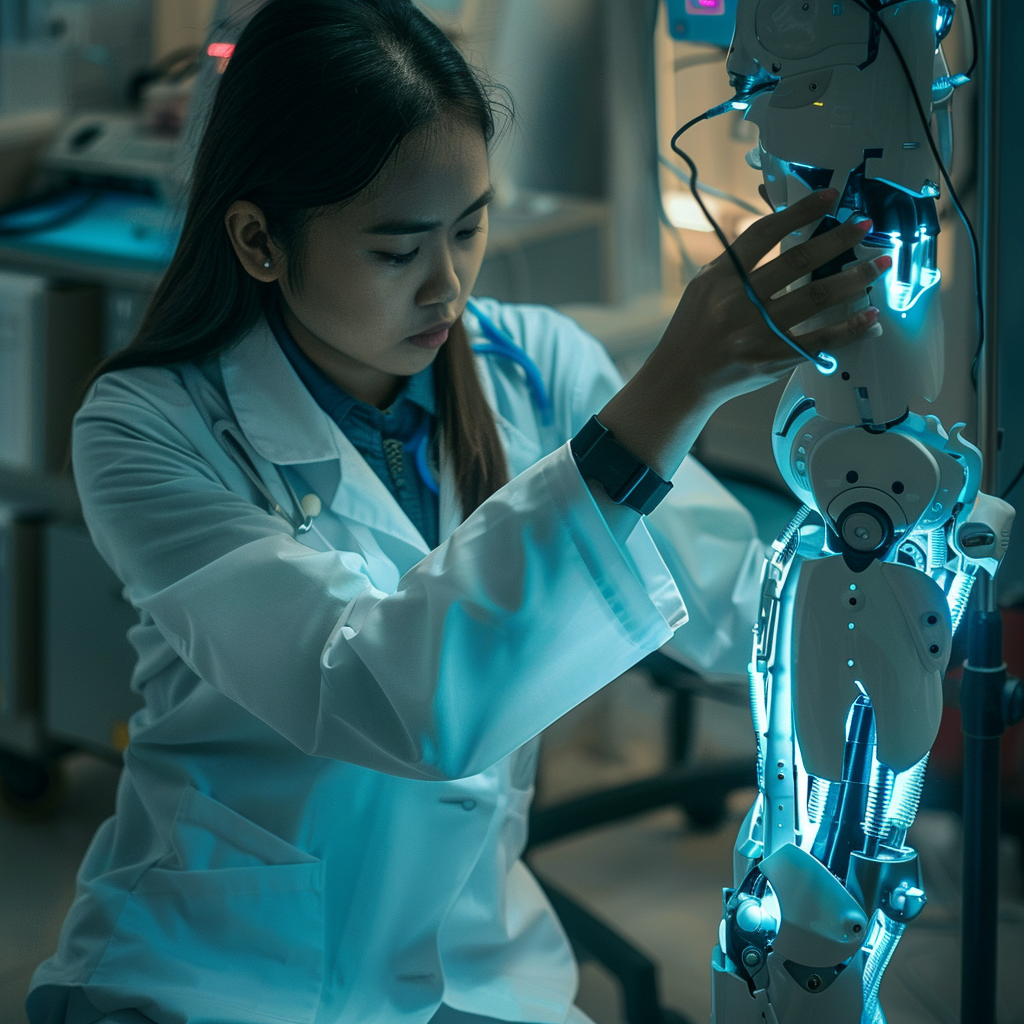

Design helps the world of healthcare continue to evolve with continuous innovation.
3. Creating Innovative and Attractive Products and Services:
Innovative design can help create new and exciting products and services for consumers. This can help improve a company's competitiveness and increase profits. For example, the innovative design of the iPhone has made Apple one of the most successful technology companies in the world.
4. Strengthen the Identity and Image of a Brand or Product:
Good design can help strengthen the identity and image of a brand or product. This can help increase brand awareness and consumer loyalty. For example, Nike's iconic swoosh logo has become one of the most famous logos in the world and is synonymous with the Nike brand.
Good design can achieve these goals by combining various elements, such as aesthetics, function, communication, and persuasion. Successful designers are those who are able to understand the needs and wants of users and then create designs that can fulfill those needs in a beautiful, functional, and effective way.
Definition of Design: Principles of Design
To be able to understand the meaning of design, you must also understand the seven basic principles of design that are the foundation of designers, including:

Contrast (Contrast)
Contrast refers to the difference between elements in a design. It can be created through differences in color, size, shape, texture, or value. Contrast can be used to draw attention to important elements, create visual interest, and organize information.
Balance (Balance)
Balance refers to the distribution of elements in a design in a way that creates a sense of balance. This can be achieved through symmetry, where elements are arranged evenly on both sides of a central axis, or asymmetry, where elements are arranged unevenly but still create a sense of balance.

Emphasis (Emphasis)
Emphasis causes certain parts of a design to stand out from other elements. Conversely it can also
used to minimize how prominent an element is (such as fine print).
Proportion (Proportion)
Proportion is the size of elements in relation to each other. Larger elements tend to be considered more important, while smaller elements are considered less important.


Hierarchy (Hierarchy)
Hierarchy refers to the importance of elements in a design. The most important element will appear to be the most important, and vice versa.
Repetition (Repetition)
Repetition reinforces ideas or perceptions. This can be done through things like using the same header format, reusing the same colors, images, or similar choices.


Rhythm (Rhythm)
The distance between elements can create a sense of rhythm, whether regular or irregular. Rhythm can be used to create a variety of emotions, including calmness (with regular rhythm) and excitement (with irregular rhythm).
Pattern (Pattern)
Patterns can refer to the repetition of design elements (as seen in wallpaper patterns). They can also refer to a set standard of how certain elements are designed (such as top navigation).

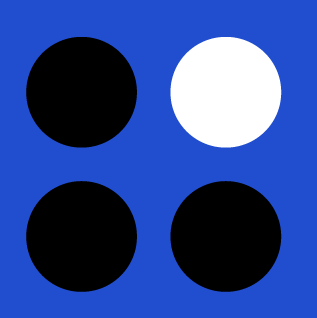
Negative Space (White Space)
White space, or negative space, refers to areas of a design that have no design elements. This space is important to make the design uncluttered, as well as to accentuate various elements.
Movement (Movement)
Movement is the way one's eye observes a design. The most important element should lead to the next most important element and so on. This can be done through positioning, emphasis, and other design principles.


Variations (Variety)
Variety creates visual interest in a design. It can be created through typography, colors, images, textures, and almost any other design element. It prevents the design from becoming monotonous and boring.
Unity (Unity)
Unity is how well the elements of a design work together. Each element should have a clear visual relationship to each other to help communicate a clear and concise message.

Definition of Design: Design Method
The definition of design must also include and discuss design methods. Design methods are procedures, techniques, aids, or tools for designing. They offer a number of different types of activities that a designer might use in the overall design process. What design methods have in common is that they are "is an attempt to publicize the personal thoughts of designers; to externalize the design process" (John Chris Jones 1970)
Exploring
Exploring is a design method that focuses on search for inspiration and new ideas. This method involves research and exploration various sources, such as current trends, culture, technology and nature. The designers use critical thinking to analyze the information gathered and identify opportunities for new and innovative designs.

A product designer who wants to design a new shoe might explore & explore the latest fashion trends, new material technologies, and the anatomy of the human foot for inspiration.
Redefining
Redefining is a design method that focuses on repetition and refinement of existing designs. This method involves analysis and evaluation existing designs to identify weaknesses and areas that can be improved. The designers used creativity and critical thinking to develop new and better solutions.

A graphic designer who wants to redefine a company logo might conduct market research to understand how the logo is received by the target audience, and then iterate on the design to make it more appealing and memorable.
Managing:
Managing is a design method that focuses on management of the overall design process. This method involves planning, organizing, and controlling all aspects of a design project, from start to finish. The designers use project management skills to ensure that the design is completed on time, within budget, and meets all requirements.

A web designer leading a team of designers in the development of a new website might use managing methods to create a project roadmap, assign tasks, and track progress.
Phototyping
Phototyping is a design method that focuses on modification and adaptation of existing designs. This method involves taking design elements from other sourcesThey take a number of things, such as photos, art, or architecture, and combine them in new ways to create unique new designs. The designers use creativity and collage skills to produce interesting and inspiring designs.

A fashion designer who wants to design a new clothing collection might use phototyping by combining photos of fabrics, patterns, and accessories to generate new design ideas.
Trendspotting:
Trendspotting is a design method that focuses on identification and utilization of emerging trends. This method involves trend monitoring in fields such as fashion, technology and pop culture, to identify opportunities for new designs that are relevant and appealing to the target audience. The designers use observation skills and critical thinking to analyze trends and predict how they will develop in the future.

An interior designer looking to design a new living room might use trendspotting to identify popular home decor trends, and then use those trends to create a modern and stylish design.
Exploring, Redefining, Managing, Phototyping, and Trendspotting are valid and useful design methods for producing innovative and effective designs. Each method has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the most appropriate method to use will depend on the context of the project and the designer's objectives.
Definition of Design: Categories of Design
The definition of design cannot be separated from categorization. The world of design is like a big, sturdy tree, with many branches reaching up. Each branch represents a unique design discipline with its own focus and purpose. These branches are connected to each other, complementing and collaborating with each other to create solutions that are innovative and beneficial to humanity.
Here are some of the main categories in design:
1. Visual Communication Design (CCD):
DKV is like a visual artist who uses visual elements such as images, illustrations, typography, and layout to effectively convey messages, information, and ideas to the audience. Imagine an eye-catching poster on the street, a memorable logo on your favorite product, or an infographic that explains complex data in an easy-to-understand way. Those are some examples of DKV designers' works that color our daily lives.
The main branches of DKV:
- Graphic Design: Focuses on designing visual elements for various media such as posters, product packaging, magazines, and websites.
- Illustration: Focuses on creating drawings and artwork for various media such as children's books, animation, and video games.
- Typography Design: Focuses on the selection and arrangement of letters to create visuals that are attractive and easy to read.
- Interaction Design: Focuses on designing interactions between users and digital products such as apps and websites.
- Motion Graphics Design: Focuses on creating engaging and informative animations and videos.
2. Interior Design:
Definition of interior design. Interior design is like an architect in the room, designing and organizing spaces to create an environment that is functional, aesthetic, and comfortable for its users. Imagine a home that feels warm and welcoming, an office that is productive and inspiring, or a restaurant that is a feast for the eyes and taste buds. Interior designers play an important role in creating optimal spaces for various activities and needs.
The main branches of interior design:
- Residential Design: Focuses on home and apartment interior design.
- Commercial Design: Focuses on interior design of commercial spaces such as offices, restaurants, and shops.
- Hospitality Design: Focusing on hotel, resort and spa interior design.
- Exhibition Design: Focuses on exhibition and museum interior design.
- Event Design: Focuses on interior design and decoration for special occasions.
3. Architectural Design:
Architectural design is like a building maestro, designing structures and conceptualizing spaces that are safe, beautiful, and durable. Imagine a towering skyscraper, a bridge connecting two lands, or a vibrant stadium. Architectural designers combine aesthetics, functionality, and construction to create landmarks that are both iconic and functional.
The main branches of architectural design:
- Building Architecture: Focuses on the design and construction of buildings such as houses, office buildings, and schools.
- Landscape Architecture: Focuses on the design and planning of outdoor spaces such as parks, playgrounds, and plazas.
- Interior Architecture: Focuses on interior design of buildings such as homes, offices, and hotels.
- Urban Architecture: Focuses on urban and regional design and planning.
- Conservation Architecture: Focuses on the preservation and restoration of historic buildings.
4. Product Design:
Definition of product design. Product design is like the creator of the things around us, perfecting the functionality and form of the things we use in our daily lives. Think ergonomic and comfortable furniture, easy-to-use electronics, educational and entertaining toys, or stylish and eco-friendly vehicles. Product designers are always looking for ways to improve the quality of life through innovation and smart design.
The main branches of product design:
- Industrial Product Design: Focuses on the design of manufactured products such as furniture, electronic equipment, and vehicles.
- Consumer Product Design: Focuses on the design of products that are used by consumers directly such as toys, home appliances, and fashion accessories.
- Digital Product Design: Focuses on the design of digital products such as apps, websites, and games.
- Interaction Design: Focuses on designing interactions between users and digital products.
- Service Design: Focuses on the design and improvement of the overall user experience of a service.
5. Fashion Design:
Fashion design is like a fashion artist, combining aesthetic beauty with functionality and comfort in clothing and accessories. Imagine an elegant evening gown paired with glittering accessories, a culturally-inspired fashion collection, or a stunning fashion show. Fashion designers stay on top of the latest fashion trends, choose luxurious materials, and design unique and beautiful pieces to create inspiring works of fashion art.
The main branches of fashion design:
- Haute Couture Design: Focuses on haute couture designs that are handcrafted using exclusive materials.
- Ready-to-Wear Fashion Design: Focuses on fashion designs that are mass-produced and easily accessible to consumers.
- Accessories Design: Focuses on designing accessories such as bags, shoes, and jewelry.
- Costume Design: Focuses on costume design for theater performances, movies, and other special events.
- Textile Design: Focuses on pattern design and fabric texture for apparel and accessories.
6. Web Design:
Web design is like an architect in the digital world, designing and developing websites and web applications that are aesthetically pleasing, functional and easy to use. Imagine an attractive and informative website, an intuitive and useful app, or a user-friendly e-commerce platform. Web designers consider aesthetics, functionality, user experience (UX), and user interface (UI) to create an optimal user experience.
The main branches of web design:
- Front-End Web Design: Focuses on developing the code and structure of the website so that it looks and functions properly in the browser.
- Back-End Web Design: Focuses on developing servers and databases that support the website.
- Web UX/UI Design: Focuses on designing user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) websites that are easy to use and intuitive.
- Responsive Web Design: Focuses on designing a website that can be accessed and seen properly on various devices such as desktops, tablets, and smartphones.
- E-commerce Web Design: Focuses on designing an online store website that is easy to use and safe for transactions.
7. Digital Product Design:
Digital product designers are like creators of innovative digital products, designing engaging and useful mobile apps, software and games. Think interactive learning apps, software that helps you with your work, or games that are fun and entertaining. Digital product designers consider aspects of user interaction, user experience and functionality to create products that are intuitive and useful.
The main branches of digital product design:
- Mobile Application Design: Focuses on designing applications that can be run on smartphones and tablets.
- Software Design: Focuses on designing software for desktops and computers.
- Game Design: Focuses on designing engaging and challenging games for multiple platforms.
- UX/UI Design: Focuses on designing user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) of digital products that are easy to use and intuitive.
- Interaction Design: Focuses on designing interactions between users and digital products.
This list is only a fraction of the various design categories that exist. The world of design continues to evolve and adapt to technology and the increasingly diverse needs of society. Each design category has its own uniqueness and contribution in creating solutions that are innovative and beneficial to humans.
Are you interested in exploring more in one of these design categories? Your talent and creativity can be the key to creating amazing design solutions and making a positive impact in the world.